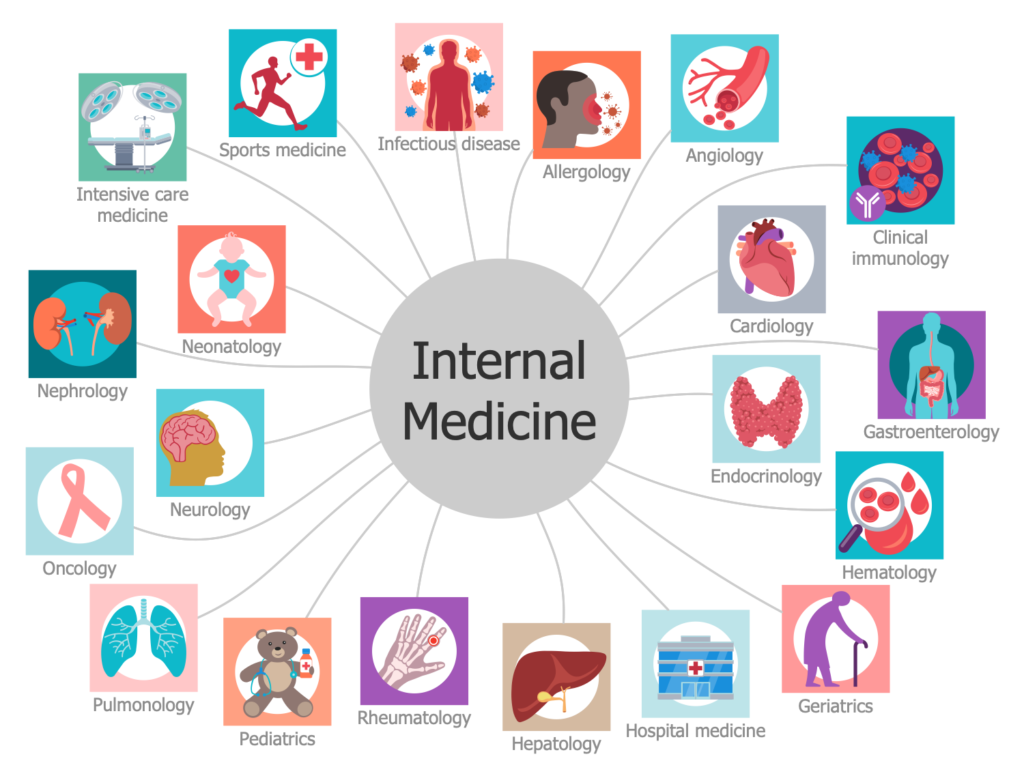
Internal medicine is a very broad specialty within medicine, and there are several subspecialties— some of which can be broken down into even more specific practice areas. Here’s a look at some of the most interrelated specialties in internal medicine and where you can find employment if you specialize in any of these areas.
Cardiology
The cardiovascular system (the heart and blood vessels) is a very complex system within the body, so it’s no surprise that cardiology can be broken down further into sub-subspecialties. Cardiologists will diagnose and treat heart conditions, but there are three main specialties within cardiology.
Advanced Heart Failure and Transplant Cardiology
Heart failure and transplant cardiology mainly deal with patients experiencing advanced or complicated heart failure, patients with special heart devices, and patients waiting on or undergoing a heart transplant. Because this is a much more complex focus of cardiology, you’re more likely to find employment in a cardiology clinic.
Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology
Cardiac electrophysiology involves evaluating heart rhythms to determine the appropriate treatment. Cardiologists in this area are sometimes called electrophysiologists because they’re trained in the heart’s electrical signals’ function, mechanism, and performance.
They see patients experiencing arrhythmias and other heart rhythm disturbances.
Electrophysiologists usually practice in cardiology group practices, so this is where you’re most likely to find employment if you specialize in this area of cardiology.
Interventional Cardiology
This subspecialty of cardiology specializes in diagnostic techniques such as imaging to evaluate the condition of the heart, arteries, and blood vessels.
Interventional cardiologists are qualified to perform minimally invasive procedures, such as catheter-based treatments for certain heart conditions.
As an interventional cardiologist, you’re most likely to find work in a cardiology group practice, but you may also find work in a hospital.
Endocrinology
Endocrinology is the subspecialty of internal medicine that focuses on the endocrine glands, hormones, and metabolic disorders. Some of the most common diseases and disorders that are associated with this subspecialty include:
● Thyroid abnormalities and diseases
● Pituitary diseases
● Hypothalamic disorders
● Gonadal disease
● Diabetes (type 2)
● Bone and lipid metabolism
Endocrinologists typically work in an endocrinology practice, but they can also find employment in multidisciplinary group practices, usually alongside nephrologists and cardiologists, because the kidneys and the heart are affected by endocrine diseases.
Hematology and Oncology
Hematology is the area of internal medicine that specializes in the blood, bone marrow, lymph nodes, and the spleen, while oncology focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of cancer (both benign and malignant tumors).
Internal medicine physicians specializing in one also have training in the other because these fields are closely related and allow for the management of a wide range of diseases.
In addition to different types of cancers, hematologists/oncologists will see patients dealing with
● Hematological malignancies
● Congenital and acquired thrombosis, hemostasis, and coagulation
● Anemias
Hematologists can find work in hospitals, hematology clinics, and oncology practices. The same goes for oncologists, though they may also find work in laboratory and academic settings. Both hematologists and oncologists are also likely to work alongside cardiologists.
Pulmonology
Pulmonology is the study of lung diseases and conditions affecting the airways that a family medicine physician doesn’t treat. As a pulmonologist, most of the conditions you’ll treat include the following:
● Sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea
● Pleurisy
● Emphysema
● Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
● Bronchitis
● Asthma
Some pulmonologists also diagnose and treat lung cancer, meaning that they also work closely with oncologists and hematologists. They may also work alongside cardiologists since many lung conditions mimic those of the heart.
With that being said, pulmonologists can find work in multidisciplinary practices that aim to provide a more holistic approach for their patients. Pulmonologists can also find employment in hospitals.
All of these physicians can also specialize with a specific age group, which are usually pediatrics (infants and children), adolescents (teens aged 13-19), or geriatrics (those over the age of 64).
However, because most of these internal medicine specialities typically have older adults as their typical patients, sub-specializing in geriatrics isn’t necessary— but specializing in pediatrics is.
Children’s bodies are very different from adults, and because internal medicine naturally deals with adults, internal medicine physicians have to acquire special skills to work with children.
Overall, these internal medicine specialties are practiced in clinics specific to the specialty, and many are even practiced in multidisciplinary group practices because they’re so closely related. So if you’re an internal medicine physician, look into specialty-specific practices and multidisciplinary group practices for employment.
RELATED TOPICS: #JOBS